Types of Roads and speed limit
Complete Guide to Road Types and Speed Limits
Learn to identify different road types, understand their characteristics, and recognize them in exam questions and know the maximum speed permited on that typr of road.
Understanding Road Classification
The Highway Code distinguishes between different types of public roads to apply specific rules for each type. Understanding these classifications is essential for safe driving and passing your driving exam.
Why road classification matters: Different road types have different speed limits, parking restrictions, and traffic rules. Being able to quickly identify the type of road you're on helps you apply the correct regulations.
Types of Roads
Portuguese roads are classified into several main categories, each with distinct characteristics and rules:
Coexistence Zones
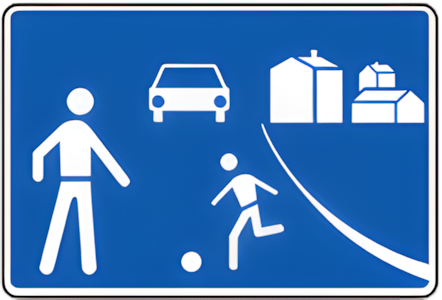
Areas where pedestrians, vehicles, and cyclists share the same space. Speed limits are very low (often walking pace) and pedestrians have priority.
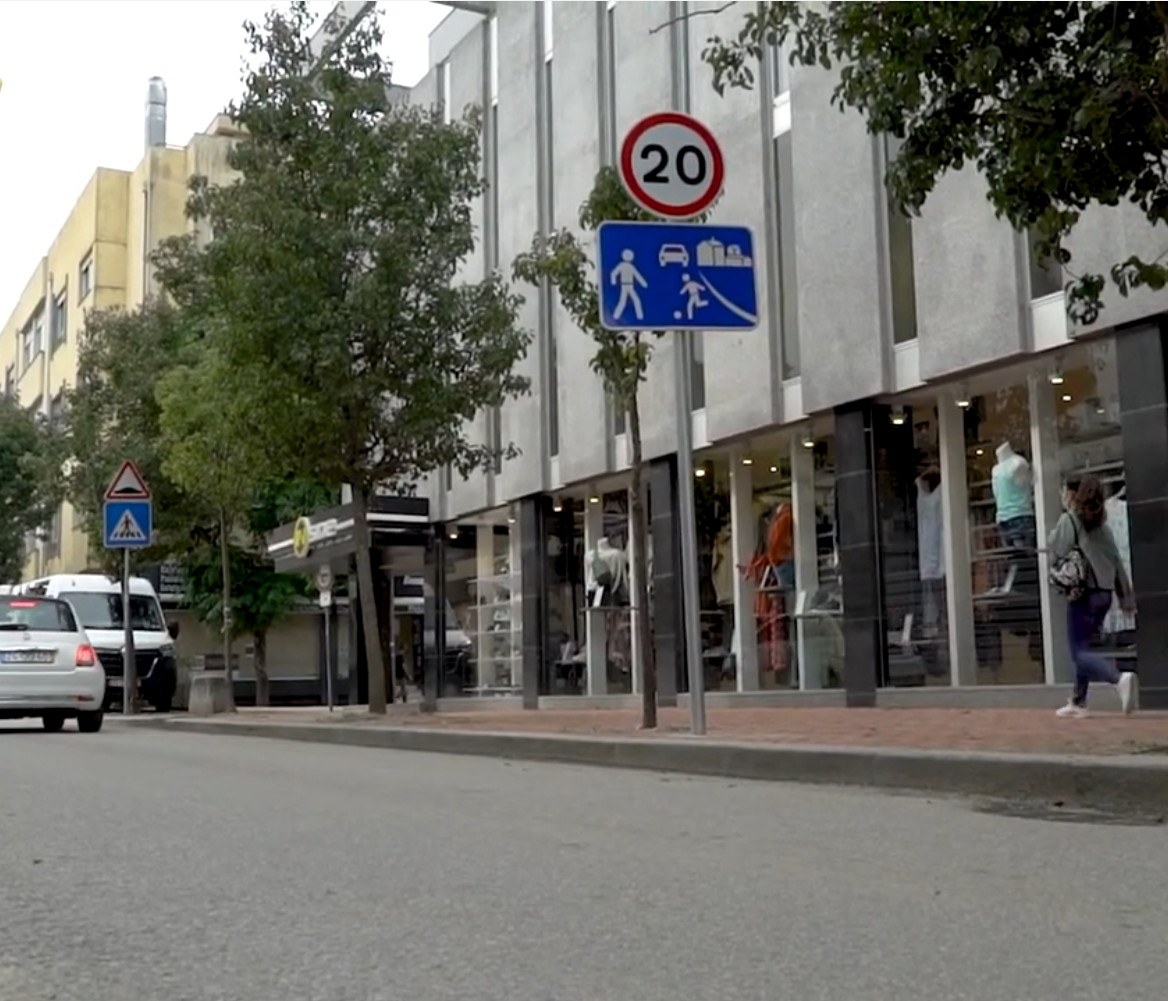

Typical coexistence zone with shared space
Inside Locality
Roads within towns and villages with buildings, pavements, and regular pedestrian activity.
Outside Locality
Roads outside towns and villages, often in rural or natural settings.
Reserved Roads
Roads reserved for automobiles and motorcycles that follow highway rules but may have different signage colors.
Details on Road types
Being able to quickly identify road types is crucial for answering exam questions correctly. Here's the details of each type:
Coexistence Zones
Highway code portugal tells about the Coexistence zone, Theses are specially designed areas where pedestrians, cyclists, and vehicles share the same space with priority given to vulnerable users. These zones have specific rules to ensure safety for all road users. According to this Article 78.º-A :
1 - The following rules must be observed in a coexistence zone:
- a) Vulnerable users may use the entire width of the public highway
- b) Playing games on the public highway is permitted
- c) Drivers must not compromise the safety or comfort of other road users, and must stop if necessary
- d) Vulnerable users must refrain from acts that prevent or unnecessarily obstruct vehicle traffic
- e) Parking is prohibited, except in locations where authorised by signage
- f) Drivers leaving a residential or coexistence zone must give way to other vehicles
2 - In regulating coexistence zones, the fundamental rules of urban design of the public highway to be applied in said zones must be observed, based on the principles of inclusive design, taking into account the needs of vulnerable users, including the definition of a single platform, where there are no physical separations of level between the spaces intended for the different modes of travel.
3 - Anyone infringing the provisions of paragraphs 1 c), d) and e) shall be punished with a fine of (euro) 60 to (euro) 300.
4 - Anyone infringing the provisions of paragraph 1(f) shall be punished with a fine of (euro) 120 to (euro) 600.
Inside Locality
Inside Locality - A zone with buildings whose limits are marked with regulatory signs. It is often called built-up area.
You're inside a Locality when you see the N1A - Beginning of Locality sign:
Examples of roads inside built-up areas:
Even if the area doesn't look urban, if you see the N1A sign, you're entering a built-up area:
Even without the sign, you can identify built-up areas by these characteristics:
- Buildings close to the road
- Pavements for pedestrians
- Regular pedestrian activity
- Parking areas and bus stops
- Street lighting
- Lower speed limits (50 km/h)
Roads Outside Locality
You're outside locality when you see the N2A - End of Locality sign:
Examples of roads outside built-up areas:
When you see the N2A sign, you're definitely outside a built-up area:
Characteristics of roads outside built-up areas:
- Few or no buildings near the road
- No pavements or pedestrian infrastructure
- Natural surroundings with vegetation
- Hard shoulders are common
- Higher speed limits (90 km/h for cars)
- Agricultural or natural landscapes
Highways
A highway (Autoestrada) is a major road made for fast travel by cars, lorries, and motorcycles. It has several lanes, no traffic lights, and can only be entered or exited at certain points. People, bicycles, tractors, and mopeds are not allowed to use it. Most highways have tolls, meaning drivers must pay to use them.
Key features Highways:
- Separated carriageways (physical barriers between directions)
- No level crossings with other roads
- Controlled access via ramps only
- No direct access to adjacent properties
- Acceleration and deceleration lanes
- Higher speed limits (120 km/h)
Physical separation examples:
No level crossings - roads cross over or under via overpasses/underpasses:
Controlled access with specific signage:
Reserved Roads
In Portugal, Roads reserved for cars and motorcycles are called (vias reservadas a automóveis e motociclos VRAM). These roads are designed mainly for motor vehicles but are not as fast or restricted as highways. VRAM share similar physical characteristics but have different signage:
Key features of Reserved roads:
- only for cars and motorcycles (bicycles, pedestrians, tractors, and other slow vehicles are not allowed.)
- No level crossings with other roads
- Controlled access via ramps only
- No direct access to adjacent properties
- Acceleration and deceleration lanes
- Medium-speed routes (Slower than highways )
Motorways and VRAM Roads
Motorways and Roads Reserved for Automobiles and Motorcycles (VRAM) share similar physical characteristics but have different signage:
Motorway - public road destined to fast traffic, with physical separation of carriageways, without level crossings nor access to marginal properties, with conditioned accesses and signalled as such;
Road reserved to automobiles and motorcycles - public road where the norms that discipline the traffic in motorway are in force and signalled as such;
How to distinguish Motorways from Roads reserved to automobiles and motorcycles
To differentiate these two types of road we have to analyse the signalling present in the image, if the sign H24 - Motorway or the H25 - Road reserved to automobiles and motorcycles is present we know the type of road. When these signs are not present we resort to other signs:
Colours of Signals
In addition to road types, Portugal has specific route classifications that indicate the importance and function of different roads:
- Main Itineraries (IP - Itinerários Principais) - The main communication routes of greatest national interest, serving as the backbone of the national road network
- Complementary Itineraries (IC - Itinerários Complementares) - Routes that establish connections of regional interest and provide access in metropolitan areas
- National Roads (EN - Estradas Nacionais) - Important roads connecting regions and municipalities
- Regional Roads (ER - Estradas Regionais) - Roads serving regional and local traffic needs
Article 18.º — Colours
— Signs indicating lane selection and allocation, advance warning, confirmation and additional signs, with the exception of bays and markers, shall have a background colour corresponding to the road network on which they are placed, in accordance with Table XX, attached, it being understood for this purpose that:4 — The signs of Selection and of allocation of lanes, of pre-signalling, of confirmation and complementary, with exception of the bays and markers, must have background colour corresponding to the road network on which they are placed according to table XX, in annex, being understood, for that effect, that:
a) To the fundamental network, constituted by main itineraries (IP), corresponds the colour green;
b) To the motorways, whatever the network in which they are integrated, corresponds the colour blue;
c) To the remaining public roads corresponds the colour white.
Road signs use specific colors to help drivers quickly identify the type of road they are on:
Main Routes (IP) - Green Signs
Green signs indicate Itinerários Principais (IP) - main national routes of greatest importance.
Motorways - Blue Signs
Blue signs indicate Motorways (Autoestradas) - high-speed roads with controlled access.
Motorway signage examples (blue background):
VRAM and other road signage examples (green/white background):
Exam Tips for Identifying Road Types
Quick Identification Guide
- Look for signs first - N1A/N2A for built-up areas, H24/H25 for motorways/VRAM
- Check surroundings - Buildings and pavements indicate built-up areas
- Look for physical separation - Barriers between directions indicate motorways/VRAM
- Check signage colors - Blue for motorways, green/white for other roads
- Note access points - Ramps with acceleration lanes indicate controlled access roads
Common Exam Scenarios
- Images showing the N1A sign = Built-up area (50 km/h limit)
- Images showing the N2A sign = Non built-up area (90 km/h limit)
- Images with blue signage = Motorway (120 km/h limit)
- Images with physical separation but no blue signs = Likely VRAM
- Images with buildings and pedestrians = Built-up area regardless of appearance
watch the video for more clarification on speed limits
Speed Limits Guide
Understanding speed limits is crucial for safe driving and passing your exam. Different vehicles have different speed restrictions based on road types and conditions.
Expo 98 Speed Table
The "Expo 98" table is a popular memory aid for speed limits. The bolded speeds (without trailer on reserved roads and with trailer on motorways) form the sequence 100, 90, 90, 80 - representing the year of Expo 98.
Quick Expo 98 Memory Tip:
Remember the sequence: 100-90-90-80 for vehicles without trailer on reserved roads and with trailer on motorways.
| Vehicle Type | L | FL | VR | AE | Other Vehicles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L = Locality (Dentro de Localidade )| FL = Outside Locality (Fora de Localidade ) | R = Reserved Roads | A = Motorways (Autoestrada) | |||||
| Without Trailer | |||||
| Passenger Cars | 50 | 90 | 100 | 120 | Motorcycles >50cc |
| Light Goods | 50 | 80 | 90 | 110 | |
| Heavy Passenger | 50 | 80 | 90 | 100 | Tricycles |
| Heavy Goods | 50 | 80 | 80 | 90 | H.G. + semi-trailer |
| With Trailer | |||||
| Passenger Cars | 50 | 70 | 80 | 100 | Motorcycles >50cc with sidecar |
| Light Goods | 50 | 70 | 80 | 90 | |
| Heavy Passenger | 50 | 70 | 90 | 90 | |
| Heavy Goods | 40 | 70 | 70 | 80 | Industrial Machines with plate |
| Other Vehicles | |||||
| Motorcycles ≤50cc | 40 | 60 | - | - | |
| Mopeds & Quadricycles | 40 | 45 | - | - | |
| Agricultural Tractors | 30 | 40 | - | - | |
| Industrial Machines (no plate) | 30 | 30 | - | - | |
| Agricultural Machines | 20 | 20 | - | - | |
| Tourist Trains | 25 | - | - | - | |
Coexistence Zones
Since January 2014, coexistence zones have a maximum speed limit of 20 km/h for all vehicles.
Complete Speed Limits Table
The complete speed limits according to Article 27 of the Highway Code:
| Vehicle Type | Built-up Areas | Motorways | Reserved Roads | Other Roads | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coexistence Zones | Other Areas | ||||
| Mopeds & Quadricycles | 20 | 40 | - | - | 45 |
| Motorcycles >50cc (no sidecar) | 20 | 50 | 120 | 100 | 90 |
| Motorcycles with sidecar/trailer | 20 | 50 | 100 | 80 | 70 |
| Motorcycles ≤50cc | 20 | 40 | - | - | 60 |
| Tricycles | 20 | 50 | 100 | 90 | 80 |
| Passenger Cars (no trailer) | 20 | 50 | 120 | 100 | 90 |
| Passenger Cars (with trailer) | 20 | 50 | 100 | 80 | 70 |
| Light Goods (no trailer) | 20 | 50 | 110 | 90 | 80 |
| Light Goods (with trailer) | 20 | 50 | 90 | 80 | 70 |
| Heavy Passenger (no trailer) | 20 | 50 | 100 | 90 | 80 |
| Heavy Passenger (with trailer) | 20 | 50 | 90 | 90 | 70 |
| Heavy Goods (no/semi-trailer) | 20 | 50 | 90 | 80 | 80 |
| Heavy Goods (with trailer) | 20 | 40 | 80 | 70 | 70 |
| Agricultural Tractors | 20 | 30 | - | - | 40 |
| Agricultural Machines | 20 | 20 | - | - | 20 |
| Industrial Machines (no plate) | 20 | 30 | - | - | 30 |
| Industrial Machines (with plate) | 20 | 40 | 80 | 70 | 70 |
Moderate Speed Requirements
Moderate speed is defined as the speed that allows a driver to stop the vehicle in a controlled manner without colliding with any obstacle, considering all circumstances.
When to Reduce Speed:
- Near pedestrian and cyclist crossings
- Near schools, hospitals, and similar establishments
- In built-up areas and coexistence zones
- Near vulnerable road users
- Near crowds of people or animals
- On steep descents
- In curves, intersections, roundabouts, and areas with reduced visibility
- On bridges, tunnels, and level crossings
- On poorly maintained or slippery roads
- Near danger signs
- During heavy traffic
Minimum Speed Limits
Only motorways have a defined minimum speed limit. All vehicles must maintain at least 50 km/h on motorways.
Important: Although the minimum speed on motorways is 50 km/h, only vehicles capable of reaching speeds above 60 km/h on level ground are permitted to use these roads.
On other road types, drivers must maintain a speed that doesn't unnecessarily obstruct other vehicles.